Backup and Backup Retention Policy Template
CIOs and IT Managers need to consider mandated compliance requirements - meets mandated compliance, ISO, and EU privacy requirements
2024 Version Updated with AI Backup and Recovery Strategy
 Question that need to be answered are:
Question that need to be answered are:
- Is our data safe in transit and at rest?
- What prevents hackers from gaining access to our data?
- Is our data properly handled, stored, and deleted?
- Who can access our data?
- What are the benchmark measurements?
- Is our data backup strategy compliant?
- Will our recovery be successful?
Order Backup Policy Backup Policy Download Selected Pages
Managing backup and recovery in today's environment is a multi-dimensional challenge with both near and long term business requirements. Recent technological developments in disk backup have had a positive impact on short term data retention requirements (see also BYOD policy). But these improvements do not replace the need to execute and deliver on a long term data retention strategy which includes:
- Business and Regulatory Requirements Demand a Long-term Plan
- Manage and Contain Your Total Cost of Ownership (TCO)
- Encrypt Your Data for Secure Long-term Retention
- Weigh the Environmental Impacts and Minimize Power and Cooling Costs
- Simplify Management of the Entire Solution
- Work from Home (WFH) Backup Strategy
IT organizations of all sizes contend with a growing data footprint with more data to manage, protect, and preserve for longer periods of time. Online primary storage, has focus a on fast low latency, reliable access to data while near-line secondary storage has a focus on low cost and high capacity.
Long-term data retention requires a combination of ultra-low cost, good performance during storage and retrieval, and reduced footprint in terms of power, cooling, floor-space and economics - also known as a small green footprint - for inactive data.
The policy now contains five (5) electronic forms and five (5) job descriptions:
Policies
- Outsourcing and Security Compliance Agreement form
- Remote Location Contact Information form
- Telecommuting Work Agreement form
- Vendor Contact Information form
- Work From Home Contact Information form
Job Descriptions
- Manager Artificial Intelligence
- Manager Compliance
- Manager Disaster Recovery and Business Continuity
- Manager Security and Workstations
- Manager WFH Support
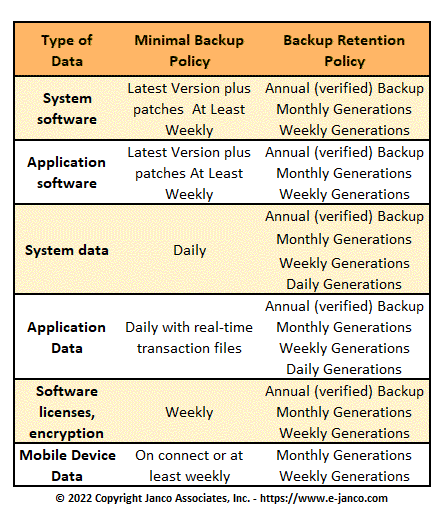
The Backup and Backup Retention Policy Template has been used to create customized policies for well over 2,000 enterprises world wide. This policy in concert with the Record Management Policy Template are must have Best Practices Tools for CIOs and IT professionals.
For example, factors that CIOs and IT professionals need to consider for backup retention include:
- Business and regulatory requirements - regulatory compliance and data preservation
- Economic and budgetary concerns - doing more with less
- Data loss prevention and information protection - protect, preserve and serve
- Environmental and business sustainment - green and economically efficient
- Maximize IT resource effectiveness and return on investment (ROI)
- Reduce total cost ownership (TCO) of IT resources and service delivery
Order Backup Policy Backup Policy Download Selected Pages
Burgeoning data continues to put pressure on legacy backup and recovery systems. Migration from tape to disk is accelerating, and innovative approaches to backup, such as target-side disk backup appliances with deduplication in an architecture provides Companies powerful capability to better manage backup and recovery and the scalability burdens associated with data growth.
A "Best of Breed" back up strategy considers how to:
- Back up critical application data - across mixed operating systems and storage configurations
- Restore desktops and mobile users quickly
- Restore systems to dissimilar hardware or virtual systems
- Back up data and system information to off site locations, so that you can quickly recover your business even from a total loss of your facility
- Leverage new cloud based backup offerings to properly secure, back up,and archive critical data
Order Backup Policy Backup Policy Download Selected Pages